| [1] 徐乐勤,丁道芳,李晓锋,等.胚胎干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2011,17(1):51-53.[2] Vadivelu S, Platik MM, Choi L,et al. Multi-germ layer lineage central nervous system repair: nerve and vascular cell generation by embryonic stem cells transplanted in the injured brain. J Neurosurg.2005;103(1):124-135.[3] Basso DM,Beattie MS,Bresnahan JC.A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats.J Neurotrauma.1995;12(1):1-21.[4] 巴迎春,范艳,王金德,等.TGF-β1和CNTF在大鼠移植神经干细胞后的损伤脊髓中的表达[J].昆明医学院学报,2012,33(3):1-7.[5] 王小莲,曾文泓,王婷,等.微囊化异种坐骨神经组织细胞移植脊髓损伤大鼠核因子κB的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(25):4619-4622.[6] 雷德强,赵洪洋,张方成,等.白介素-10对脊髓损伤后炎症影响的研究[J].山东医药,2008,48(4):6-7. [7] 廖维宏,张光铂. 进一步加强脊髓损伤修复研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2003,13(9):517-519. [8] Suzuki H, Taguchi T, Kato Y, et al.Transplantation of neurospheres derived from bone marrow stromal cells promotes neurological recovery in rats with spinal cord injury.Med Mol Morphol.2011;44(3):131-138.[9] Penkala K,Kawa M,Baumert B,et al.Functional improvement of injured retina following the adjuvant stem cellbased therapy.Preliminary report.Klin Oczna.2011;113(46):117-121.[10] Keski-Oja J, Koli K, Melchner H. TGF-beta activation by traction? Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14(12): 657-659.[11] 李云,彭春,王廷华.嗅鞘细胞移植脊髓全横断损伤大鼠大脑皮质运动区转化生长因子β表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(19):3534-3537.[12] 贾赤宇,陈璧.TGFβ1对瘢痕形成的影响[J].中华整形烧伤外科杂志,1999;15(1):72-73.[13] 周健,张富国,潘寒松,等. TGF-β蛋白在急性脊髓损伤大鼠中的研究[J].医学研究杂志,2008,37(8):31-33.[14] Lane MA, Truettner JS, Brunschwig JP, et al.Age-related differences in the local cellular and molecular responses to injuryin developing spinal cord of the opossum, Monodelphis domestica.Eur J Neurosci. 2007;25(6):1725-1742.[15] Martinou JC,Le Van Thai A,Valette A,et al.Transforming growth factor beta 1 is a potent survival factor for rat embryo motoneurons in culture. Brain Res Dev Brain Bes. 1990;52 (1-2): 175-181.[16] O'Brien MF, Lenke LG, Lou J, et al. Astrocyte response and transforming growth factor-beta localization in acute spinal cord injury. Spine. 1994;19(20):2321-2329.[17] Kim JH, Min KJ, Seol W, et al. Astrocytes in injury states rapidly produce anti-inflammatory factors and attenuate microglial inflammatory responses.J Neurochem. 2010; 115(5):1161-1171. [18] Pineau I, Sun L, Bastien D,et al. Astrocytes initiate inflammation in the injured mouse spinal cord by promoting the entry of neutrophils and inflammatory monocytes in an IL-1 receptor/MyD88-dependent fashion. Brain Behav Immun. 2010; 24(4):540-553. [19] Kreutzberg GW.Microglia,the first line of denfence in brain pathologies. Arzneimittelforschung. 1995;45(3A):357-360. [20] Flanders KC,Ren RF,Lippa CF.Transforming growth factor-betas in neurodegenerative disease. Prog Neurobiol. 1998;54(1):71-85. [21] Wang X, Chen W, Liu W, et al. The role of thrombospondin-1 and transforming growth factor-beta after spinal cord injury in the rat. J Clin Neurosci. 2009; 16(6):818-821.[22] Hamada Y, Ikata T, Katoh S, et al. Effects of exogenous transforming growth factor-beta 1 on spinal cord injury in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1996;203(2):97-100. [23] Kohta M, Kohmura E, Yamashita T. Inhibition of TGF-beta1 promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Neurosci Res.2009;65(4):393-401.[24] Harauz G, Ishiyama N, Hill CM, et al. Myelin basic protein-diverse conformational states of an intrinsically unstructured protein and its roles in myelin assembly and multiple sclerosis. Micron.2004; 35(7):503-542.[25] 吴波,孙磊,任先军.少突胶质前体细胞移植治疗对大鼠脊髓损伤轴突髓鞘化的影响[J].中华创伤杂志,2010,26(11):1035-1039.[26] 张涛,沈忆新,芦磊磊,等.硫酸软骨素酶ABC对大鼠脊髓损伤后轴突髓鞘化和胶质瘢痕的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013, 27(2):145-150.[27] Atkinson S, Li YQ, Wong CS. Changes in oligodendrocytes and myelin gene expression after radiation in the rodent spinal cord. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.2003;57(4): 1093-1100.[28] Fukuda A, Fukuda H, Swanpalmer J, et al. Age-dependent sensitivity of the developing brain to irradiation is correlated with the number and Vulnerability of progenitor cells. J Neurochem.2005; 92(3): 569-584.[29] Kotter MR, Li WW, Zhao C, et al. Myelin impairs CNS remyelination by inhibiting oligoden- drocyte precursor cell diferentiation. J Neuro-sci. 2006;26(1): 328-332. |

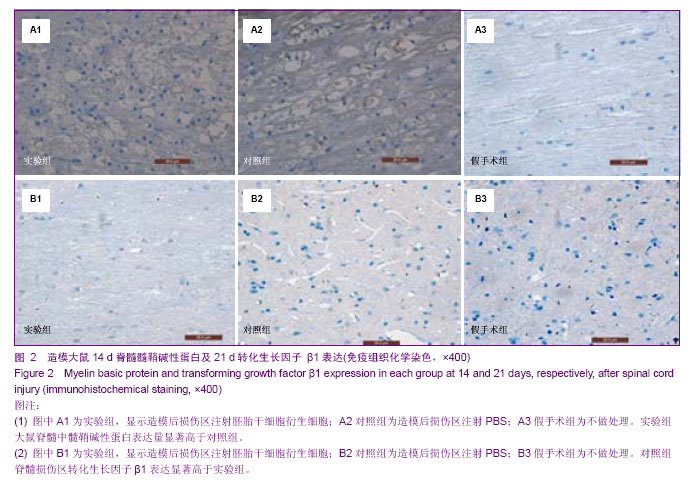
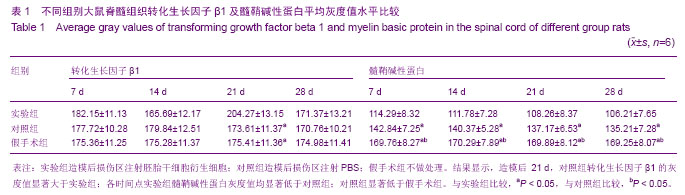
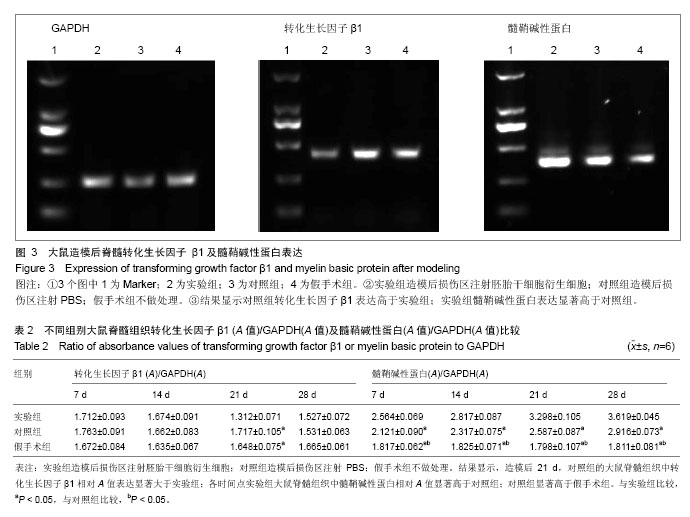
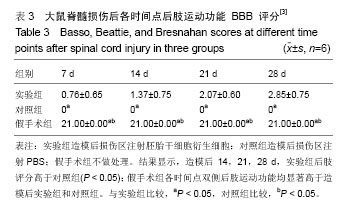
.jpg)
.jpg)